In the Cattle feeding and nutrition have been recently introduced, and are spreading, the dynamic systems of rationing. These systems simulate, in a mechanistic way, the effects of intake, rumen fermentations, intestinal digestion, absorption and metabolism as function of animal performances. The bottom line on which statist models of rationing are based, instead, says that nutritional values are intrinsic features both of the animal that ingest it and of the diet it is part of. Consequently, diet characteristics are the result of the weighted average of fixed (static) nutritional parameters a priori attributed to each ingredient included.
The most known and field used among the dynamic models is CNCPS, utilized by the NDS Professional software platform (version 3). It is proving to be very effective in evaluations for every Cattle category diets (dairy and beef), with very high accuracy levels of forecast. It is a decision-making support tool of great interest.

In the matter of Buffalos feeding, rationing criteria adopted are very much connected to systems developed for Cattle, especially the INRA system (1988). Dairy Buffalos rationings, in fact, are borrowed by the dairy Cattle approach: only different empirical adjustments were made on the basis of productive responses. Steps forward were made in the definition of Buffalos needs but assessment models of their nutritional demand still tightly depend on the Cattle ones.
It is understandable then the need for formulation tools based on effective physiological and metabolic characteristics of Buffalos (for some aspects very different from the other Ruminants livestock) and specifically destined to them.
This is also proved by the fact that in the last few years, several attempts were done (both in Italy and elsewhere) in order to evaluate Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System (CNCPS) with the purpose of nutritional evaluation of diets for Dairy Water Buffalo, using both CNCPS 5.0 and CPM Dairy.
In general, the conclusions reached tell us that the CNCPS model is more suitable in the evaluation of Cattle performances; that means that some of its aspects are not applicable to Buffalos and that some adjustments and a greater number of validations for its adaptation to these animals are needed.
In particular, among the factors which were identified as a limit for the accuracy, are indicated the kind of animal effect (metabolic status), digestive characteristics and dynamics (retention time, rumen fermentation and intestinal digestion), milk production allowed both by Metabolizable Energy and Metabolizable Proteins.
Dynamic model in Buffalos diet formulation
On the basis of what it has been described, having in hands the CNCPS model license and thanks to the tight collaboration with the Dept. of Animal Science of Cornell University, an evaluation work was conducted by the Research and Development Department at RUM&N. It was related to requirements evaluation and productive prediction on diets for dairy Mediterranean Buffalo cows. Two were the goals: first of all identify aspects of the model that have to be adapted to specific Buffalos characteristics, then adjust the biological model in order to make it usable in practice for this kind of Ruminant.
Several aspects of the model were detected and must be aligned to peculiar physiological and metabolic Buffalos characteristics. Among them we can list:
- Dry matter intake prediction;
- Requirements for basal metabolism maintenance in heat neutrality;
- Passage rate for liquids and solids and related retention time;
- Energetic partitioning between milk production and body reserves;
- Passage and intestinal digestibility;
- Efficiency of conversion of metabolizable proteins into milk proteins.
Keeping unchanged the CNCPS model framework, we brought adjustments and modifications to some of its sub-models, on the basis both of knowledge concerning specific metabolic Buffalos characteristics and experimental outcomes published.
WB-NCPS
Thus, was born the WB-NCPS, acronym of Water Buffalo Net Carbohydrate and Protein System; it is a dynamic model both for the evaluation of diets and the performances allowed for Mediterranean Buffalo.
Its goal is to
predict the requirements and the utilization of protein and
energy, on the basis of different influences that could modify demands and use
of feeds for productions. Metabolizable energy and protein (ME and MP) requirements vary for
animal type, environment characteristics, management and feeding
system.
ME and MP contributions to the diet are based on the quality and quantity of feed intake, rumen fermentation of carbohydrates and proteins degradation, microbial yield, the passage and intestinal absorption of nutrients and on partitioning among different physiological functions. The value of the system is its ability of both identifying, with high efficiency, those factors which limit Buffalos performances and quantifying their effects in an independent way.
WB-NCPS system simulates nutrient supply effects, rumen fermentations, intestinal digestion, absorption and metabolism on performances.
The uses you can make are:
- predict the effects on productions and milk quality of the diet;
- predict the effects of the modifications on a digestive and metabolic level on animal performances;
- evaluate and balance the recipe;
- satisfy the requirements and estimate productions for every environmental and management conditions;
- illustrate and predict the effects of some gastrointestinal parameters on feeds utilization;
- compare dynamic model evaluations with those made by traditional static systems.
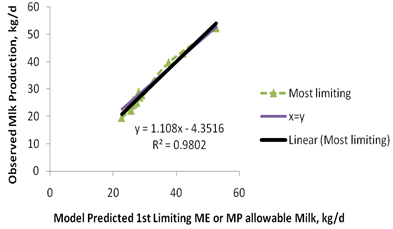
The new model has been evaluated for the precision and accuracy in prediction Buffalos milk production using 12 data sets coming from studies published and collected in several Italian Dairy Water Buffalo farms.
The relations between the observed vs. predicted milk by the model on the basis of ME and MP supply, are following described:
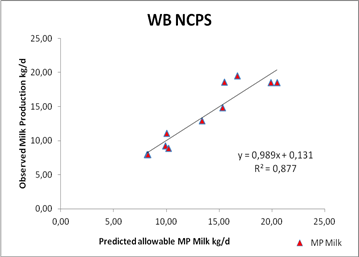
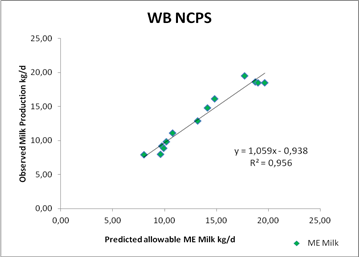
On the basis of these evaluations, the accuracy prediction for milk production is good and, in any case, greater than what it was previously obtained using CNCPS 5.0, CPM Dairy or other static systems (INRA 1988).
Implications
Evolution of biological dynamic models is a continuous process which proceeds in parallel with our biological knowledge improvement. Rationing software must develop on the same way in order to be able to adopting more and more developed models and to meet the needs of more and more demanding and prepared nutritionists and professionals.
WB-NCPS model, available in NDS Professional platform, was primarily developed in order to offer a tool able to formulate more precise rations for Lactating and non-lactating Dairy Buffalo.
The interface, which was specifically conceived for user assistance, is able to facilitate its use, rapidity in the data entry process and software stability. It can be used every day by researchers, technicians and field nutritionists with improvement in prediction accuracy and increase of use efficiency, compared with static systems available today.