There are seven macromineral elements considered:
− Calcium (Ca)
− Phosphorus (P)
− Magnesium (Mg)
− Potassium (K)
− Sodium (Na)
− Chlorine (Cl)
− Sulfur (S)
Additionally, the Dietary Cation-Anion Difference (DCAD) involving Na, K, Cl and S is considered in ration formulation for lactating and dry cows.
Laboratory wet chemistry methods must be used to accurately measure total concentrations, since NIR is not practically and universally applicable to detect total element concentrations across a wide variety of feeds and supplements used in rations.
Bioavailability (efficiency of absorption)
Not all of the various mineral elements in rations are available for absorption. Therefore, NDS Professional adopted the NRC (2001) approach of using an absorption coefficient to supply adequate mineral elements in rations. Where research results permitted, an absorption coefficient was assigned for the mineral element in concentrates, forages, and inorganic mineral sources. Sufficient data were not available for the NRC committee to use this approach for sulfur (S). The 2001 NRC expresses absorption coefficients as proportions (i.e., 0 to 1), then NDS proposes the same approach.
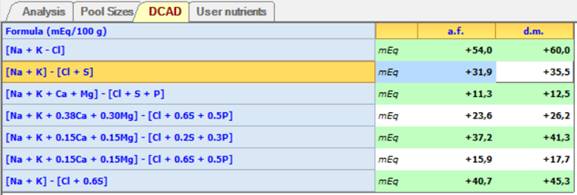
Dietary Cation-Anion Difference (DCAD)
Dietary Cation-Anion Difference (DCAD) influences systemic acid-base status and the metabolism of other nutrients such as Ca. In NDS DCAD is expressed for each feed as milliequivalents of major fixed cations minus major fixed anions per 100 grams of dietary dry matter, according to several formulas:

Anyway, the equation used most commonly in the field is: mEq [(K + Na) – (Cl + S)]/100 grams
When considering DCAD in ration formulation, the first step we suggest is to analyze the K, Na, Cl and S contents of all feed ingredients used in ration formulation by wet-chemistry analysis to insure accuracy. The contents of these elements are variable within feed type, especially for forages within and among farms, and are heavily influenced by fertilization practices and other agronomic and weather-related factors.
The second step is to meet the nutrient requirements (e.g., grams per day) for the defined animal description for K, Na, Cl and S.
Note: in NDS the addition of common white salt (NaCl) and KCl do not alter the DCAD of a ration because they are neutral salts. Addition of elemental sulfur (such as the flowers of sulfur), has no physiological influence on of the target animal because it is biologically un-/non-reactive as delivered via the ration.